Add-ons
Содержание:
Rules view
The Rules view lists all the rules that apply to the selected element, ordered from most-specific to least-specific. See above.

See Examine and edit CSS for more details.
The Layout view displays the box model of the page. If the page includes any sections using either the Flexbox display model or CSS Grids, this view shows the Flexbox or Grid settings used on the page.

To learn more about the Layout view, see Examine and edit the box model. Note that before Firefox 50, the box model view did not appear in the «Layout view» tab, but had its own tab.
When you are editing in the Rules view, you can see the changes you have made in the Changes view.

The Computed view shows you the complete computed CSS for the selected element (The computed values are the same as what getComputedStyle would return.):

To learn more about the CSS declarations listed in this view, see .
Starting with Firefox Developer Edition version 77, the Compatibility view shows CSS compatibility issues, if any, for properties applied to the selected element, and for the current page as a whole. It shows icons for the browsers that do support the properties, and notes properties that are experimental or deprecated.

- Click the name of the property to open the reference article for that property on MDN Web Docs. The «Browser compatibility» section of the article gives details of browser support for the property.
- In the All Issues section, click the name of the element that uses the property to select that element in the inspector. If more than one element has a given property applied to it, click the triangle to show all the occurrences.
- To configure the set of browsers you want the Compatibility view to check for, click Settings at the bottom of the panel.

Untick the checkbox for any browser you are not interested in. As new browser versions are released, the version numbers in this list will be updated.
The Fonts view shows all the fonts in the page along with editable samples.

See View fonts for more details.
The Animations view gives you details of any animations applied to the selected element, and a controller to pause them:

See Work with animations for more details.
Tabs
In Firefox 49 onwards, a Tabs page is available in — this provides a complete list of all the debuggable tabs open in the current Firefox instance.

Each tab entry has a Debug button next to it — when clicked, this will open up a toolbox specific to that tab, allowing you to debug that tab’s contents.

Note that this feature isn’t that immediately useful to debugging desktop tabs — you can open up a toolbox to debug a tab easily enough already — but this will become far more useful when starts to support remote debugging, and this page can begin to list tabs available for debugging on mobile device browsers, simulators, etc. See баг 1212802 for the latest on this work.
Network throttling
If you do all your development and testing using a very fast network connection, users may experience problems with your site if they are using a slower connection. In Responsive Design Mode, you can instruct the browser to emulate, very approximately, the characteristics of various different types of networks.
The characteristics emulated are:
- Download speed
- Upload speed
- Minimum latency
The table below lists the numbers associated with each network type, but please do not rely on this feature for exact performance measurements; it’s intended to give an approximate idea of the user experience in different conditions.
| Selection | Download speed | Upload speed | Minimum latency (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPRS | 50 KB/s | 20 KB/s | 500 |
| Regular 2G | 250 KB/s | 50 KB/s | 300 |
| Good 2G | 450 KB/s | 150 KB/s | 150 |
| Regular 3G | 750 KB/s | 250 KB/s | 100 |
| Good 3G | 1.5 MB/s | 750 KB/s | 40 |
| Regular 4G/LTE | 4 MB/s | 3 MB/s | 20 |
| DSL | 2 MB/s | 1 MB/s | 5 |
| Wi-Fi | 30 MB/s | 15 MB/s | 2 |
To select a network, click the list box that’s initially labeled «No throttling»:

Скачивание и установка
Все, кто хочет испробовать возможности Firefox Developer Edition, смогут скачать установочный файл с официального сайта компании. Ссылка: https://www.mozilla.org/ru/firefox/developer/
На открывшейся странице предстанет краткое описание браузера и его возможностей, с которыми можно ознакомиться более подробно, кликнув на одну из них.
Для скачивания и установки браузера следует выполнить следующий порядок действий: 1. Кликните по значку загрузки.
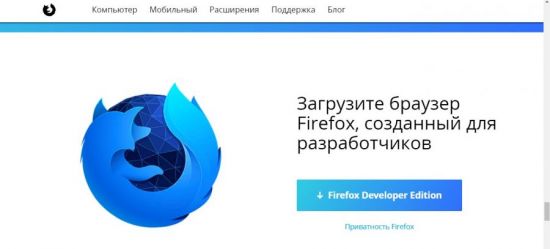
2. На компьютер будет загружен автоматический установщик, который следует запустить.
3. Дождитесь окончания установочного процесса.
Теперь на ваш компьютер установлен Mozilla Firefox Developer Edition. По своему дизайну он немного отличается от обычной версии. При первом запуске откроется вкладка с описанием встроенных возможностей. О каждой из них можно узнать подробно, кликнув соответствующую кнопку.
Сам браузер выполнен в темном стиле. Главная вкладка имеет привычный интерфейс, котрый пользователь может настроить под свой вкус.
При желании можно совершить синхронизацию и перенос закладок из других браузеров.
Для того чтобы воспользоваться инструментами программы, необходимо открыть меню и кликнуть по разделу «Веб-разработка».
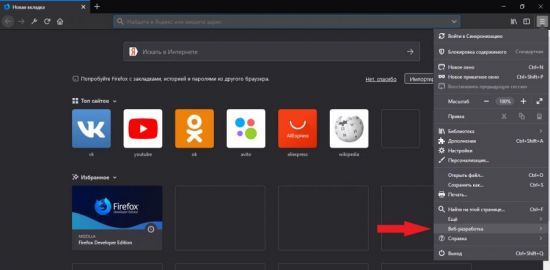
Откроется окно со всеми доступными инструментами разработчика. Кликнув по любому из них, пользователь запустит инструмент и сможет приступить к работе с ним.
Для быстрого доступа к возможностям программы предусмотрены горячие клавиши. Зажав комбинацию из 2–3 кнопок, можно запустить процесс, не обременяя себя переходом в нужный раздел меню.
HTML Tutorials
- Introduction to HTML
- This module sets the stage, getting you used to important concepts and syntax, looking at applying HTML to text, how to create hyperlinks, and how to use HTML to structure a webpage.
- MDN HTML element reference
- A comprehensive reference for HTML elements, and how the different browsers support them.
- Creating a Simple Web Page with HTML
- An HTML guide for beginners that includes explanations of common tags, including HTML5 tags. Also includes a step-by-step guide to creating a basic web page with code examples.
- HTML Challenges
- Use these challenges to hone your HTML skills (for example, «Should I use an <h2> element or a <strong> element?»), focusing on meaningful markup.
- Multimedia and embedding
- This module explores how to use HTML to include multimedia in your web pages, including the different ways that images can be included, and how to embed video, audio, and even entire other webpages.
- HTML tables
- Representing tabular data on a webpage in an understandable, accessible way can be a challenge. This module covers basic table markup, along with more complex features such as implementing captions and summaries.
- HTML forms
- Forms are a very important part of the Web — these provide much of the functionality you need for interacting with websites, e.g. registering and logging in, sending feedback, buying products, and more. This module gets you started with creating the client-side parts of forms.
- Tips for authoring fast-loading HTML pages
- Optimize web pages to provide a more responsive site for visitors and reduce the load on your web server and Internet connection.
Документация по типам
- Руководство веб-разработчика
- Руководство веб-разработчика предоставляет полезные пошаговые материалы, которые помогут вам в полной мере использовать веб-технологии для выполнения ваших задач и реализации ваших идей.
- Учебные материалы для веб-разработчиков
- Перечень учебных материалов позволит вам пошагово изучить API, технологии и расширить свой кругозор в области веб-технологий.
- Справочные материалы (en-US)
- На данной странице будут представлены ссылки на всю справочную информацию, имеющуюся в MDN; а пока можно использовать ссылки на веб-технологии из левой части данной страницы.
The split console
You can use the console alongside other tools. While you’re in another tool in the Toolbox, just press Esc or press the «Toggle split console» button in the . The toolbox will now appear split, with the original tool above and the web console underneath.
As usual, works as a shorthand for the element currently selected in the Inspector:
 When you use the split console with the debugger, the console’s scope is the currently executing stack frame. So if you hit a breakpoint in a function, the scope will be the function’s scope. You’ll get autocomplete for objects defined in the function, and can easily modify them on the fly:
When you use the split console with the debugger, the console’s scope is the currently executing stack frame. So if you hit a breakpoint in a function, the scope will be the function’s scope. You’ll get autocomplete for objects defined in the function, and can easily modify them on the fly:

Интерпретатор командной строки
Вы можете выполнять JavaScript-код в реальном времени, используя командную строку в Web-консоли.

Для ввода выражений просто введите в командную строку и нажмите Enter. Для ввода выражений, состоящих из нескольких строк, используйте комбинацию ShiftEnter вместо Enter.
Введённое выражение отобразится в окне сообщений, с выводом результата последующей строкой:

Вы можете получить доступ к переменным на странице; это могут быть как внутренние переменные например в объекте , так и переменные, добавленные с помощью Javascript кода — например с помощью :

У командной строки есть функциональность автоподстановки: начните вводить несколько начальных букв — и появится всплывающее окно с возможными вариантами завершения команды:
 Нажмите Enter или Tab, чтобы принять нужную подсказку, перемещайтесь вверх/вниз с помощью стрелок к другим вариантам подсказок или просто продолжайте набирать текст, если вам не подходит ни один из вариантов.
Нажмите Enter или Tab, чтобы принять нужную подсказку, перемещайтесь вверх/вниз с помощью стрелок к другим вариантам подсказок или просто продолжайте набирать текст, если вам не подходит ни один из вариантов.
Консоль выдаёт подсказки из области видимости текущего активного фрейма. Это значит, что если вы уже достигли точки останова в функции, то у вас будут доступны автоподстановки только для объектов, которые находятся в одной области видимости с этой функцией.
Вы можете получать такие же подсказки для элементов массива:

Вы можете объявить ваши собственные переменные, и в последующем обращаться к ним:

Командная строка запоминает введённые ранее команды: чтобы перемещаться вперёд и назад по истории, используйте стрелки вниз и вверх на клавиатуре.
Начиная с Firefox 39, эта история сохраняется между сессиями. Чтобы очистить историю, используйте .
Если страница содержит встроенные iframes (en-US), вы можете использовать команду чтобы изменить область видимости в консоли на область определённого iframe, и после этого вы сможете выполнять функции, которые содержит объект document в этом iframe. Существует три способа выбрать iframe используя :
Вы можете передать DOM-элемент для определённого iframe :
Вы можете передать CSS селектор для определённого iframe:
Вы можете передать глобальный объект Window для определённого iframe:
Для переключения контекста видимости обратно к окну верхнего уровня, введите без аргументов:
Предположим у нас есть документ, который содержит iframe:
В этом iframe определена новая функция:
Вы можете переключиться на контекст iframe например так:
Сейчас вы сможете видеть, что глобальный объект Window это теперь наш iframe:
 и сможете выполнить вызов функции, определённой в этом iframe:
и сможете выполнить вызов функции, определённой в этом iframe:

{{ page(«/en/Using_the_Web_Console/Helpers», «The commands») }}
Edit rules
If you click on a declaration or a selector in the Rules view you can edit it and see the results immediately. You can also Tab through the different existing properties and values, and start editing them by pressing Enter or Space. To add a new declaration to a rule, click on the last line of the rule (the line occupied by the closing brace).
As you start typing a property name, you’ll see a list of autocomplete suggestions. Press Tab to accept the current suggestion or Up and Down to move through the list. The default choice is the most common property that starts with the letters you’ve typed. For example, here the user has typed «c» and the default choice is «color»:

If you enter an invalid value for a property when editing it, or an unknown property name, a yellow alert icon appears besides the declaration.
Edits that you make in the Rules view are reflected in the Style Editor, and vice versa. Any changes you make are temporary: reloading the page will restore the original styling.
While you’re editing CSS, the context menu you’ll see is the normal one for working with editable text:

CSS variable names will auto-complete depending on the variables defined in the CSS. If you enter into a property value and then type a dash (), any variables you have declared in your CSS will then appear in an autocomplete list, which shows a color swatch so you can see exactly what color each variable choice is storing (bug 1451211).
In addition, hovering over a CSS variable name brings up a tooltip showing what color value is stored in that variable (bug 1431949).

You can use the arrow and page up/down keys (along with others) to increase/decrease numeric rules while editing:
- The Up arrow increments values by 1 — for example, «1px» changes to «2px».
- Shift + Up/Down increments or decrements values by 10.
- Ctrl + Up/Down (on Linux and Windows) or Alt + Up/Down (on Mac) increments or decrements values by 0.1.
- Shift + Page up/Page down increments or decrements values by 100.
When you are editing the rules in the rules view, you can see the changes you have made in the Changes pane.

Note: You can view changes made to the rules view only. If you edit the CSS using the Style Editor, the changes will not be shown in the changes pane.
Also remember, as noted above, that changes you make to the CSS rules are temporary and will be reset if you reload the page.
If you are satisfied with the changes you have made, you can copy the new settings to page the edited rule into your stylesheet. Right-click on the changes panel and select Copy Rule from the context menu.

The Copy Rule command copies the entire element, class, or id definition, including any unchanged rules and the rules that describe your changes. For example, copying the changes in the preceding image, you get the following:
Подключение
Есть два способа подключения: «Экран подключения» и «WebIDE».
На отлаживающем Firefox в меню «Разработка» есть пункт «Соединиться…». Кликните его и увидите страницу:

Введите номер порта, заданный для отлаживаемого и нажмите «Connect». В отлаживаемом увидите диалог для подтверждения подключения:
 Нажмите»OK» и вернитесь в отладчик. Появится такая страница:
Нажмите»OK» и вернитесь в отладчик. Появится такая страница:

- Под «Available remote tabs» (Доступные удалённые вкладки) находится список всех вкладок отлаживаемого. Кликните в одну для соединения Инструментов разработчика Firefox c ней.
- Под «Available remote add-ons» (Доступные удалённые дополнения) находится список всех дополнений на отлаживаемом. Кликните в один для соединения Инструментов разработчика Firefox.
- Под «Available remote processes» (Доступные удалённые процессы) — список процессов, запущенных в Firefox. Кликните «Main process» (Главный процесс) для соединения Инструментов разработчика с самим браузером.
На отлаживающем Firefox откройте WebIDE кликните «Select Runtime»/»Remote Runtime» (Удалённый Runtime):
 Вас попросят предоставить имя компьютера и порт. Введите «localhost:6000» или другой номер порта, если прислушивается иной порт (смотря какой вы указали).
Вас попросят предоставить имя компьютера и порт. Введите «localhost:6000» или другой номер порта, если прислушивается иной порт (смотря какой вы указали).
На отлаживаемом Firefox появится предупреждение:
Кликните OK. WebIDE подключится к главному процессу. Если вы захотите подключиться к вкладке, то в списке слева выберите нужную вкладку, которую будете отлаживать.

Подключение инструментов разработчика
Если вы откроете инструменты разработчика с помощью или аналогичных пунктов меню, они будут нацелены на документ, размещённый на текущей активной вкладке. Но вы также можете прикрепить инструменты к множеству других целей, как в текущем браузере, так и в разных браузерах или даже на разных устройствах.
- about:debugging
- Отладка надстроек, вкладок контента и рабочих, работающих в браузере.
- Подключите инструменты разработчика к Firefox, работающему на устройстве Android.
- Подключение к iframes
- Подключите инструменты разработчика к конкретному iframe на текущей странице.
- Подключение к другим браузерам
- Подключите инструменты разработчика к Chrome на Android и Safari на iOS.
This Firefox
The This Firefox tab combines the features of Extensions, Tabs, and Workers into a single tab with the following sections:
- Temporary Extensions
- Displays a list of the extensions that you have loaded using the Load Temporary Add-on button.
- Extensions
- This section lists information about the extensions that you have installed on your system.
- Service Workers, Shared Workers, and Other Workers
- There are three sections on this page that deal with Service Workers, Shared Workers, and Other Workers.

Whether internal extensions appear in the list on this page depends on the setting of the preference. If you need to see these extensions, navigate to and make sure that the preference is set to .
Extensions
With the Load Temporary Add-on button you can temporarily load a web extension from a directory on disk. Click the button, navigate to the directory containing the add-on and select its manifest file. The temporary extension is then displayed under the Temporary Extensions header.
You don’t have to package or sign the extension before loading it, and it stays installed until you restart Firefox.
The major advantages of this method, compared with installing an add-on from an XPI, are:
- You don’t have to rebuild an XPI and reinstall when you change the add-on’s code;
- You can load an add-on without signing it and without needing to disable signing.
Once you have loaded a temporary extension, you can see information about it and perform operations on it.

You can use the following buttons:
- Inspect
- Loads the extension in the debugger.
- Reload
- Reloads the temporary extension. This is handy when you have made changes to the extension.
- Remove
- Unloads the temporary extension.
Other information about the extension is displayed:
- Location
- The location of the extension’s source code on your local system.
- Extension ID
- The temporary ID assigned to the extension.
- Internal UUID
- The internal UUID assigned to the extension.
- Manifest URL
- If you click the link, the manifest for this extension is loaded in a new tab.
If you install an extension in this way, what happens when you update the extension?
- If you change files that are loaded on demand, like content scripts or , then changes you make are picked up automatically, and you’ll see them the next time the content script is loaded or the popup is shown.
- For other changes, click the Reload button. This does what it says:
- Reloads any persistent scripts, such as
- Parses the file again, so changes to , , or any other keys take effect
The permanently installed extensions are listed in the next section, Extensions. For each one, you see something like the following:

The Inspect button, and the Extension ID and Internal UUID fields are the same as for temporary extensions.
Just as it does with temporarily loaded extensions, the link next to Manifest URL opens the loaded manifest in a new tab.
Note: It’s recommended that you use the Browser Toolbox, not the Add-on Debugger, for debugging WebExtensions. See Debugging WebExtensions for all the details.
The Add-ons section in about:debugging lists all web extensions that are currently installed. Next to each entry is a button labeled Inspect.
Note: This list may include add-ons that came preinstalled with Firefox.
If you click Inspect, the Add-on Debugger will start in a new tab.
See the page on the Add-on Debugger for all the things you can do with this tool.
Справочники
- Справка по HTML
- HTML состоит из элементов, каждый из которых может быть изменён некоторым количеством атрибутов. HTML-документы связаны между собой ссылками.
- Справка по HTML-элементам
- Просмотр списка всех элементов HTML.
- Справка по HTML-атрибутам
- У элементов в HTML есть атрибуты. Это дополнительные величины, которые настраивают элементы или управляют их поведением различными способами.
- Глобальные атрибуты
- Глобальные атрибуты могут быть указаны для всех элементов HTML, даже тех, которые не указаны в стандарте. Это означает, что любые нестандартные элементы обязаны по-прежнему разрешать эти атрибуты, даже если эти элементы делают документ несовместимым с HTML5.
- Строчные и блочные элементы
- Элементы HTML являются обычно «строчными» или «блочными». Строчный элемент занимает только пространство, ограниченное тегами, которые его определяют. Блочный элемент занимает все пространство своего родительского элемента (контейнера), тем самым создавая «блок».
- Типы ссылок
- В HTML различные типы ссылок могут использоваться для установления и определения связи между двумя документами. Элементы-ссылки, типы которых могут быть заданы, включают в себя , и .
- Поддержка медиа-форматов с помощью HTML-элементов audio и video
- Элементы и позволяют вам воспроизводить аудио и видео. Эти элементы предоставляют браузерную альтернативу аналогичным возможностям, которые есть в Adobe Flash и других плагинах.
- Виды HTML-контента
- HTML состоит из нескольких видов контента, каждый из которых разрешено использовать в определённых контекстах и запрещено в других. Так же, у каждого есть набор других категорий контента, которые они могут содержать, и элементы, которые могут или не могут использоваться в них. Это руководство по таким категориям.
- Режим совместимости и стандартный режим
- Историческая справка по режиму совместимости и стандартному режиму.
Setup tab
Firefox supports debugging over USB with Android devices, using the about:debugging page.
Before you connect:
- Enable Developer settings on your Android device.
- Enable USB debugging in the Android Developer settings.
- Enable Remote Debugging via USB in the Advanced Settings in Firefox on the Android device.
- Connect the Android device to your computer using a USB cable.
If your device doesn’t appear in the lefthand side of the about:debugging page, try clicking the Refresh devices button.
If it still doesn’t appear, it may be because the link between your Android device and your computer is not authorized yet. First make sure you have installed Android Debug Bridge from Android Tools on your computer in order for it to be able to connect to your device. Next, disable every debugging setting already activated and repeat the steps described before. Your device should show a popup to authorize your computer to connect to it — accept this and then click the Refresh devices button again. The device should appear.
Note: You do not need to install the full Android Studio SDK. Only adb is needed.
To start a debugging session, first open the page that you wish to debug and then click Connect next to the device name to open a connection to it. If the connection was successful, you can now click the name of the device to switch to a tab with information about the device.

The information on this page is the same as the information on the This Firefox tab, but instead of displaying information for your computer, it displays the information for the remote device with the addition of a Tabs section with an entry for each of the tabs open on the remote device.
Note: If the version of Firefox on your remote device is more than one major version older than the version running on your computer, you may see a message like the following:

In Firefox 76 and above, the message can look like the following:

See for more information.
In the image above, there are three tabs open: Network or cache Recipe, Nightly Home, and About Nightly. To debug the contents of one of these tabs, click the Inspect button next to its title. When you do, the Developer Tools open in a new tab.

Above the usual list of tools, you can see information about the device you are connected to, including the fact that you are connected (in this example) via USB, to Firefox Preview, on a Pixel 2, as well as the title of the page that you are debugging, and the address of the page.
Starting in Firefox 78, the URL bar is editable, so that you can change the URL used by the browser on the remote device, by typing in Firefox for Desktop. You can also reload the page by clicking the Reload button next to the URL bar, and (starting 79), navigate backward or forward in the browsing history with the Back and Forward buttons.
You can connect to a Firefox Debug server on your network, or on your debugging machine using the Network Location settings of the about:debugging page.

Enter the location and port on which the debugger server is running. When you do, it is added to the Network locations list along with the devices, as shown below:

Подробности
Фаерфокс Девелопер Едишн представляет собой продвинутую во многих аспектах версию браузера, с рядом улучшений. Представляем вашему вниманию краткое описание для всех ключевых моментов:
- Повышенная производительность – использование модернизированной версии CSS-движка, с помощью которого достигается более высокая скорость работы.
- Управление CSS-сеткой – визуализация сетки с возможностью ее «горячего» редактирования.
- Редактор фигур – он предназначается для детальной наладки в визуальном редакторе параметров clip-path вместе с shape-outside.
- Инструменты разработчика – множество функций, которые окажутся полезными при создании и отладке веб-страниц.
- Панель шрифтов – просмотр подробной информации относительно задействованных шрифтов, которые были задействованы в конкретной информации.
А об одном из указанных ранее достоинстве мы поговорим более детально.
Инструменты разработчика
Именно им стоит уделить особенное внимание, ведь браузер все же ориентирован именно на веб-разработчиков. Компания Mozilla предоставила им широкий спектр возможности по части создания сайтов и последующей их доработке
Хотелось бы остановиться на этих моментах более детально:
- Инспектор – изучение и редактирование кодов HTML и CSS на странице.
- Консоль – отображение всей необходимой информации о веб-странице странице с возможностью исполнения JavaScript.
- Отладчик – отслеживание корректности работы JS.
- Сеть – возможность мониторинга сетевых запросов вместе с их влиянием на скорость загрузки интернет-страниц.
- Панель хранилища – просмотр сохраненной пользовательской информации (кэш-файлы, данные куки, история просмотров и так далее), с возможностью ее редактирования и даже добавления.
- Визуальное редактирование – наглядная отстройка анимаций, размещения и форматирования текстов и прочих элементов.
- Редактор JS – написание, редактирование и исполнение JS-скриптов прямиком на открытой интернет-странице.
- Производительность – инструменты для оптимизации.
- Память – мониторинг потребления памяти с возможностью нахождения «слабых мест».
- Веб-аудио – возможность изучения и настройки Web Audio API.
- Режим адаптивного экрана – просмотр правильности отображения интернет-страниц на различных устройствах (ПК, смартфоны, Smart TV и так далее).
- Редактор стилей – инструменты для настройки CSS по своему усмотрению.
Firefox channels
Firefox is available in five channels.
Each night we build Firefox from the latest code in mozilla-central. These builds are for Firefox developers or those who want to try out the very latest cutting edge features while they’re still under active development.
This is a version of Firefox tailored for developers. Firefox Developer Edition has all the latest developer tools that have reached beta. We also add some extra features for developers that are only available in this channel. It uses its own path and profile, so that you can run it alongside Release or Beta Firefox.
Every four weeks, we take the features that are stable enough, and create a new version of Firefox Beta. Firefox Beta builds are for Firefox enthusiasts to test what’s destined to become the next released Firefox version.
After stabilizing for another four weeks in Beta, we’re ready to ship the new features to hundreds of millions of users in a new release version of Firefox.
Firefox ESR is the long-term support edition of Firefox for desktop for use by organizations including schools, universities, businesses and others who need extended support for mass deployments.